Infrared thermal modules convert temperature data into a visual, quantifiable format, enabling machine vision systems to detect defects, monitor conditions, and optimize processes based on thermal metrics.
How the Best Infrared Thermal Modules Enhance Machine Vision for OEMs
Article from | Raytron Microelectronics
In today’s highly automated industrial landscape, OEMs face a critical challenge: traditional machine vision systems can 'see' but cannot 'feel' temperature. This limitation hinders the timely detection of equipment failures, product defects, and process anomalies. Infrared thermal modules convert temperature data into a visual, quantifiable format, enabling machine vision systems to detect defects, monitor conditions, and optimize processes based on thermal metrics. This ensures the product's quality, process stability, and equipment reliability. Thermal modules are now widely used in sectors like high-end electronics manufacturing, new energy battery testing, industrial automation, and precision equipment maintenance.
What are Infrared Thermal Modules and Thermal Sensors?
The thermal module is a core component of an integrated infrared thermal detector and imaging system that converts infrared radiation emitted by an object into a visual heat map or precise temperature data. Its core technology is infrared technology, which uses infrared radiation emitted by objects to measure the surface temperature of objects, thereby achieving thermal imaging. Accurately reflect tiny temperature fluctuations through high resolution, high frame rate and NETD.

SE5 Series Infrared Thermal Module
Integrating Raytron Microelectronics’ SE5 series infrared thermal module into a machine vision system significantly improves the ability to detect hidden defects, assess product quality, and perform detailed inspections, thanks to the excellent imaging capabilities of the ceramic package, 12μm pixel size, 30Hz high refresh rate, and 1284x1280 resolution. In addition, the SE5 series infrared thermal module adopts a non-blocking correction algorithm, with a delicate and clean image. It is equipped with a self-developed ASIC chip, which achieves small size, light weight, and low power consumption, meeting the needs of portability and integrated installation. For example, at the quality inspection station for lithium battery tab welding, a machine vision system with an integrated thermal imaging module can perform full-range temperature measurement of the solder joints. By analyzing the uniformity of temperature distribution in thermal images, the system can accurately identify localized low temperatures caused by cold solder joints or abnormally high temperatures caused by overheating. These defects, which are invisible under visible light, are directly identified as defective by the thermal vision system and triggered to be removed by the sorting mechanism.
|
Technical Specifcations |
SE5 1280 |
|
Detector Type |
Uncooled VOx Infrared Detector
|
|
Resolution
|
1280×1024
|
|
Frame Rate
|
30hz |
|
Pixel Size |
12um
|
|
Spectral Range
|
8~14μm |
|
NETD
|
≤40mK@25?,F#1.0,25Hz
|
What are the Key Advantages of Thermal Machine Vision Cameras
- Precision and Accuracy: The core advantage of infrared thermal imaging modules lies in expanding temperature measurement from “points” to “surfaces.” They can detect minute temperature differences and identify defects by analyzing the uniformity of the temperature field distribution across the entire target area. For example, in semiconductor packaging inspection, a thermal module can accurately capture local thermal resistance anomalies caused by internal voids. This defect from the inside out is completely undetectable under visible light but is critical to product life.
- Increased Efficiency: Through infrared thermal sensors, the machine vision system can monitor temperature in real time without direct contact with the object being detected, perform real-time temperature map analysis, and directly determine good or bad quality and trigger sorting without pausing. This non-invasive approach reduces equipment wear and accelerates the inspection process, enabling OEMs to improve production efficiency while maintaining high-quality standards.
- Reliability in Harsh Conditions: According to a study by Nikhil Ghag, Harshad Sonar, Rahul Sawant, and Kirti Bankapalli (2025), thermal modules perform excellently under extreme conditions, remaining stable in complex environments such as high temperatures, high reflections, and metal splashing. This makes them highly valuable in industrial inspection and other demanding environments.
What are the Applications of Thermal Camera for Machine Vision
Infrared thermal modules have widespread applications in OEM machine vision systems. Below are some key areas where thermal machine vision cameras are making an impact:
- Automated Quality Control: On the production line, thermal modules can be used to detect product defects, such as overheated components or parts that have not been properly cooled. This enhances the accuracy and speed of the quality control process.
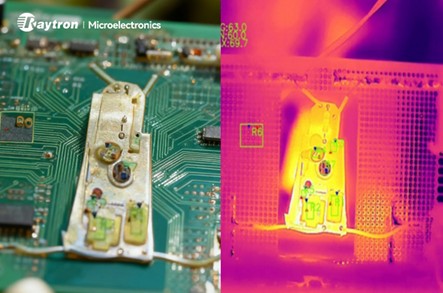
Comparison of Visible Camera and Infrared Thermal Imaging for Monitoring the Temperature of PCB
- Robotics and Automation: Granting robots “thermal touch”. In scrap sorting, robots can utilize the temperature difference between recently stopped components and the environment to identify and pick up metal residues accurately. Before precision assembly, by detecting whether the preheating temperature of components meets standards, thermal imaging helps avoid assembly stress caused by thermal expansion and contraction.
- Industrial Inspection: The core lies in predictive maintenance. By continuously monitoring the temperature trends of motor bearings and distribution cabinet terminals, the system can provide early warnings before fault-induced overheating occurs. When combined with vibration analysis, the temperature data offers a more comprehensive diagnostic perspective on equipment health

Comparison of Visible Camera and Infrared Thermal Imaging for Industrial Inspection
- Environmental Monitoring: OEM-developed environmental monitoring systems, such as HVAC systems or weather stations, can leverage the non-contact temperature measurement capabilities of thermal camera modules to provide more accurate data.
For OEM manufacturers seeking breakthroughs, integrating infrared thermal modules is a strategic necessity to tackle the complex challenges of industrial automation with thermal technology. The infrared thermal module precisely addresses the core limitation of traditional machine vision, which cannot sense temperature, by enhancing inspection dimensions, optimizing production processes, and empowering intelligent systems.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow
Featured Product

