New Optical Delay Line Stage Series, Based on Air Bearings, Released by PI
Lower pitch/yaw angular errors and the near-perfect straightness and flatness performance of air bearings deliver precise measured results, surpassing mechanical linear stages.
Auburn, MA - PI, the global leader in nanopositioning motion control, introduces a series of air bearing-based optical delay line stages. The ADL25 through ADL300 delay lines provide delays from 0.16 to 2 nanoseconds with time resolution down to 0.035 femtoseconds.
Research on ultra-fast processes is continuously gaining importance - it is critical to understand various scientific and technological phenomena, such as chemical and biological processes, molecular dynamics, and quantum effects. The 2023 Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded for research into attosecond pulses of light. In time-resolved spectroscopy, dynamic processes in materials and chemical compounds can be studied precisely. With the help of ultra-short pulse lasers, changes can be made visible, with time scales down to the attosecond range. Due to the limited speed of light, making the light travel a longer distance to its destination, will change the timing. A precise control in the femtosecond and even attosecond range is made possible by so called delay-line stages. The mechanical precision required for controlling these minute time increments is made obvious, when one considers that a delay of 0.1 femtoseconds is achieved with a positional change of only 14 nanometers.
Historically, delay lines have relied on mechanical bearing linear stages and motion controllers. However, the geometric performance limitations of mechanical bearings can impact the precision of measured results, and velocity constraints may restrict the number of experiments within a given time slot.
Issues, such as straightness and flatness errors, lead to deviations from the beam path, causing shifts in the output beam along the X and Y axes. Yaw errors introduce changes in the incidence angle, further displacing the output beam in both X and Y directions.
In contrast, air bearings present notable advantages over their mechanical counterparts. They exhibit significantly lower pitch/yaw angular errors and near-perfect straightness and flatness. This ensures that, during pumping and probing at different delays, the beam remains at or very close to the Region or Point of Interest. Additionally, higher velocities and quicker settling times facilitate the collection of more data, allowing researchers to conduct up to twice as many experiments - a crucial benefit when faced with limited beam line time.
Featured Product
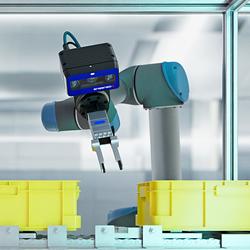
3D Vision: Ensenso B now also available as a mono version!
This compact 3D camera series combines a very short working distance, a large field of view and a high depth of field - perfect for bin picking applications. With its ability to capture multiple objects over a large area, it can help robots empty containers more efficiently. Now available from IDS Imaging Development Systems. In the color version of the Ensenso B, the stereo system is equipped with two RGB image sensors. This saves additional sensors and reduces installation space and hardware costs. Now, you can also choose your model to be equipped with two 5 MP mono sensors, achieving impressively high spatial precision. With enhanced sharpness and accuracy, you can tackle applications where absolute precision is essential. The great strength of the Ensenso B lies in the very precise detection of objects at close range. It offers a wide field of view and an impressively high depth of field. This means that the area in which an object is in focus is unusually large. At a distance of 30 centimetres between the camera and the object, the Z-accuracy is approx. 0.1 millimetres. The maximum working distance is 2 meters. This 3D camera series complies with protection class IP65/67 and is ideal for use in industrial environments.
