The sophisticated integration of perception sensors, autonomous navigation, manipulation, and artificial intelligence in Swift warehouse robots enables maximum picking productivity across single pick, trays, and totes.
 Autonomous Mobile Manipulation Robots and e-Commerce Fulfillment
Autonomous Mobile Manipulation Robots and e-Commerce Fulfillment

Tom Galluzzo, Founder | IAM Robotics
Tell us about IAM Robotics & your role with the company.
At IAM Robotics, we make autonomous robots that navigate and pick items in e-Commerce fulfillment centers. Our robots use computer vision to drive around by themselves, find individual items and bring them to a warehouse worker.
I founded IAM Robotics along with my friend Vladimir Altman. We used to work at Carnegie Mellon together at the National Robotics Engineering Center (NREC). Now I'm leading the development of our robots to do new warehouse tasks and to deploy our robots on a larger scale for bigger customers.
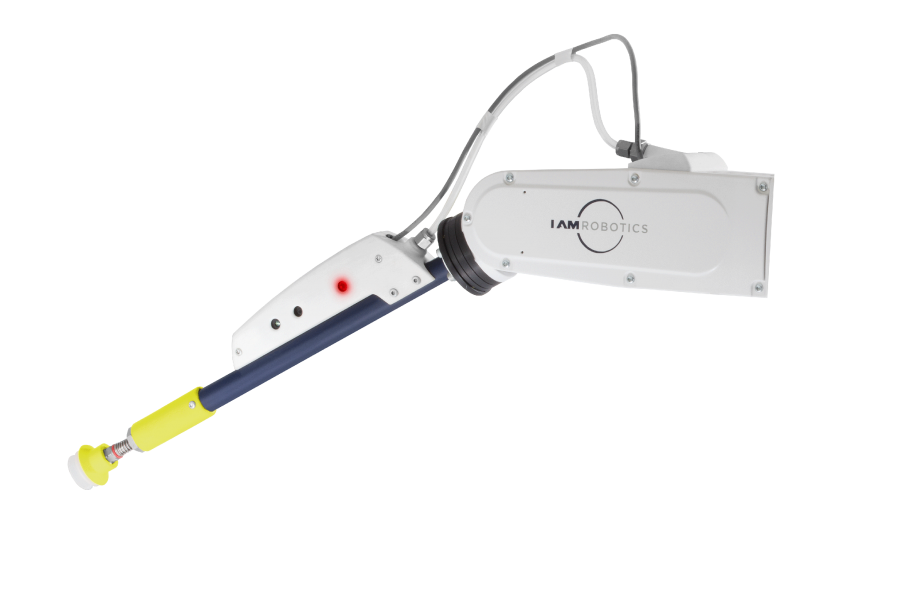
What are some of the main advantages of using Robots in e-Commerce fulfillment?
Our robots allow the fulfillment workers to increase their productivity by not having to walk around the facility to get things. It's backbreaking labor and most people can't do it that long. Warehouse workers have a higher injury rate than a lot of other jobs, and our robots really alleviate that pain, by going to collect items for people. That's the main advantage. It makes people more efficient to work with a team of robots and that allows the warehouse to sell more items. The end result is that the fulfillment company can make more money and keep their people happy.
Please give us an overview of a mobile manipulation robot?
Mobile manipulation robots combine two capabilities, one is autonomous navigation, the other is autonomous grasping. Our robots have a wheeled mobile base, which is automatically able to navigate from point A to B by using visual sensors that allow them to sense where they are in their environment. The robots also are equipped with an arm and end-effector which allows them to physically pick up different items. The key to making mobile manipulation robots work is vision. The robots are able to see what they are doing and they need to be able to see because things are not precisely placed in a warehouse environment, so the robot must use vision to compensate for that.
What are the challenges around developing a mobile manipulation robot?
The biggest challenge is the software. Anyone can put an off-the-shelf industrial robot arm on a wheeled base, but it’s very hard to develop the algorithms necessary to coordinate the two capabilities. Specifically, you need vision sensor and perception algorithms that allow the robot to adjust for things being uncertainly positioned, which includes the robot itself.
Tell us about your Swift Product Suite and how it differs from other autonomous mobile robotic solutions?
The Swift Product Suite is different from other autonomous mobile robotic solutions because of its unique combination of navigation, perception, and manipulation. IAM Robotics’ Swift Product Suite offers a complete order fulfillment solution, which includes a Swift robot that travels autonomously into warehouse storage areas, finds the inventory locations, individually identifies objects, and picks the objects. Swift can travel autonomously through the warehouse, finding and identifying products, and then picking them up with one of a variety of end effectors.
The Swift Product Suite was built from the ground up for fully automating the piece-picking process for e-commerce order fulfillment. The sophisticated integration of perception sensors, autonomous navigation, manipulation, and artificial intelligence in Swift warehouse robots enables maximum picking productivity across single pick, trays, and totes. There is no need to invest heavy CAPEX in changing existing warehouse infrastructure for companies that wish to augment their person-to-goods model. Companies may also flexibly configure Swift warehouse robots today or in the future for a goods-to-person model that optimizes pick, pack and ship processes for e-commerce.
Our solution is adaptable and has the ability to change as business needs change (i.e. peak seasons can be augmented with human labor). Low capital investment with no expensive replacements or extensive planning is required to adapt the Swift Product Suite to warehouse or distribution center environments.
Can you share a general overview of the process from planning to deployment of a robot and its support systems?
From an early stage in our sales process, we like to have a full understanding of what our clients want to achieve and accomplish in their warehouse automation. These discussions include discussions around their demand profiles, current operations, product attributes, upstream and downstream systems, and others. From these discussions, the IAM Robotics team pulls together models and simulations to help clients visualize how our solution will impact their business operations. Once the Swift Product Suite is deployed into a client’s operations, we have regular meetings to discuss client innovation improvements, preventive maintenance, and new features and capabilities deployment schedules.
Where do you see the robots and material handling for e-Commerce 5 or 10 years down the road?
I think we’ll certainly see robots all over the warehouse, helping with all critical functions: receiving, picking, packing, shipping, and even stocking. Beyond that, I’m sure we will start to see outdoor robots integrated with the warehouse. This will include driverless delivery vehicles, drones and more!
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow
Featured Product

