The process of training robots through virtual Reality is referred to as Imitation learning. This technique assists a robot to absorb several skills in a low-cost and low risk environment. The robots can easily mimic the human, guided by machine learning algorithms.
 Industrial Robots Stepping in to Help Economies with Inadequate and Expensive Labor Force
Industrial Robots Stepping in to Help Economies with Inadequate and Expensive Labor Force

Ankush Yadav | The Insight Partners
Industrial robots is a gigantic industry and is radically changing since its introduction in the past decades. Industrial robots are in general referred to as robotic arms, which perform diverse motions such as up and down motion, and pick and place. Moreover, these robots can be controlled to do different functions, such as transportation, searching, assembly, targeting, and inspection. The industrial robots are mainly comprised of six fundamental elements including, end-of-arm tool, dynamic system, actuators, controller, sensor, and feedback devices.
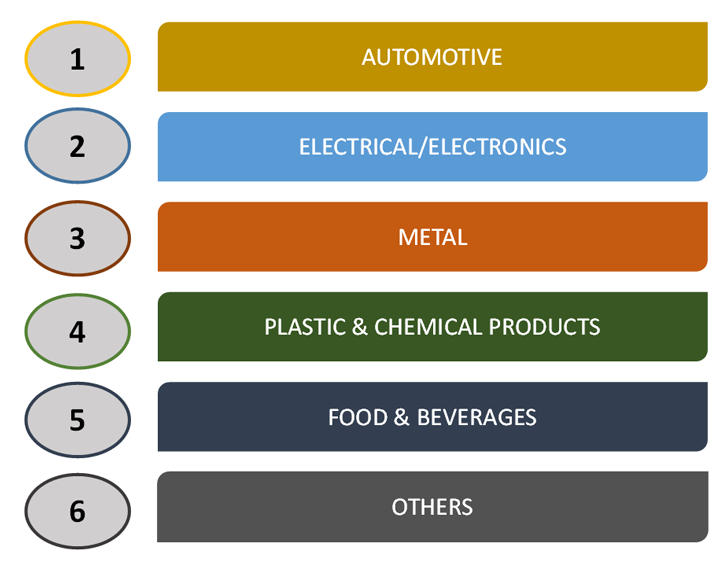
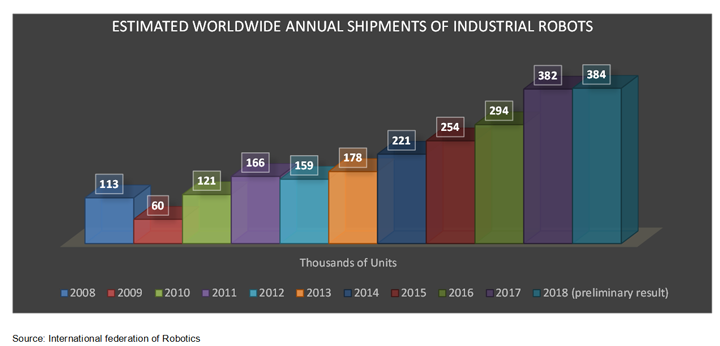
Robotics technology has been applied to a wide variety of sectors with a high economic and social impact. Since the past few years, it has been one of the significant elements of industrial manufacturing automation, where over 1.5 million robots are currently operating. In the year 2017, around 380,000 industrial robots was sold all across the globe. Different industries witnessing implementation of industrial robots in their processes includes automotive, electrical, metal plastic & chemical, and food & beverage among others. Besides the implementation of these robots in the manufacturing industries, there is an increasing propagation of these robots in service and field sectors such as agriculture, health, mining, forestry, and logistics, among others. Robot technology already represents a significant market with a growing impact factor, both in economic and in societal terms, such as productivity, employment, and working conditions.
These days the industrial robotics market coupled with artificial intelligence, big data and other such technologies are becoming more recurrent into existence. It is expected that such robots will not only boost productivity but will also provide advanced smart assistance to humans in the coming years. The players and governments of certain economies are significantly investing in the development of industrial robots integrated with artificial intelligence. The integration of artificial intelligence in industrial robots will also reduce the intervention of humans, which will be beneficial for countries with the inadequate and expensive labor force.
However, challenges prevail where robots and humans work together collaboratively, which would require a consistent communication as well as due regard for safety and reliability. The development of strong methodologies for recognition, human interaction and navigation will linger, at a modest rate rather than in bounds and leaps. One of the major possibility may impose towards the progress of personal robots that would perform human chores. The terror of genetically engineered robots or sub-humans taking over human roles is worth considering but preferably not approvable. Nevertheless, heavy duty maneuvers in industries and mines, hazardous environments, mineral exploration, and a multitude of other applications would be automated by the use of robotics. However, the necessity for sophisticated machine acumen could be severely lessened.
Although industrial robots can prove extremely effective and bring a positive ROI for a company, the deployment of industrial robots might require a high capital investment. The factor has limited the adoption of industrial robots, particularly by SMEs. SMEs located in certain developing economies are still unable to obtain the benefits of automation as they find labor inexpensive in comparison to the deployment of industrial robots. Also, these robotic systems require timely maintenance, and replacement of sensors, which incur a huge cost. Further, when any company decides to go through the process of automation, higher capital investment is required at the initial stage. Moreover, deployment of industrial robots, as a part of the automation process includes around 25% of the overall cost. At times, the investors are uncertain about the ROI, which restricts the deployment of robots and results in postponement of investment. Additionally, with disinvestment in several industries, there is an availability of refurbished robots resulting in limiting the demand for the new robots.
One of the main obstacle faced during installation of industrial robots is the expertise and time. Companies such including Embodied Intelligence and OpenAI are using Virtual Reality to train robots. In this process, human teleoperators perform certain actions in a virtual environment, which is then copied by the robots. The process of training robots through virtual Reality is referred to as Imitation learning. This technique assists a robot to absorb several skills in a low-cost and low risk environment. The robots can easily mimic the human, guided by machine learning algorithms.
Advancements in technologies such as artificial intelligence, big data, and machine learning have bolstered the adoption of industrial robots. Further, easy installation and lower costs is expected to drive their installation in SMEs. With the increase in skills, traditional industrial robots are likely to be replaced by more intelligent industrial robots.
The content & opinions in this article are the author’s and do not necessarily represent the views of RoboticsTomorrow
Featured Product

